☼ Examine how learning takes place and reflects on
effectiveness
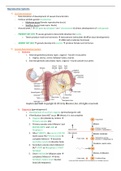
How learning takes place
- the brain is designed to learn and learning shapes the brain.
- the more active the brain is, the stronger the connections between
neurons become
- with practice strong pathways develop and some actions come
automatically
- to create a studying pathway in your brain for learning, you need to:
Learn, solve problems, recall, read, think, calculate, reflect and write.
- learning something new needs repetition.
☼ Study styles as preferred way of approaching tasks
- every person’s brain is different, because of different wiring.
- each brain is unique and prefers learning in a specific way.
- you need to find the learning style that suits the way in which your
brain is wired
, ☼ Study strategy to approach a specific task in the light of c) Read
perceived demands
- Read the material under the heading with the purpose of getting the answer to your question. Read
with concentration.
- Use a study method that allows you to read actively, ask and
answer questions, practise, repeat and revise what you learn. - Identify the main ideas and highlight or underline them.
The SQ3R method adheres to these requirements: - Read sections at a time and stop to ask questions. Jot down notes and ask yourself what you just
read. If you can answer your question, read on. If not, look it over again.
SURVEY ~ QUESTION ~ READ ~ RECITE ~ REVIEW
- A good practice for more difficult reading is to do an outline of chapter in your notes. By leaving
extra space you can fill in details during the class lecture.
a) Survey
- Make note of new vocabulary and write definitions in your notes
- Go through the chapter quickly.
- Glance at the chapter title, the introduction, headings, and summary
d) Recite
paragraphs, if any. Notice any pictures, diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.
Read any bold print. - This step requires that you recite out loud the answer to the question you asked prior to
- Previewing your text gives you some background about topics you may reading a section of the text. Say it in your own words. If you find you cannot answer your
have never encountered before. You pick up general information. You
know where to find information. You gain a better idea of how the question, go back and look for the answer, then try again.
information is organized and presented. It opens a place in your brain
- Besides answering your questions, look away from the book and try to state in your own
where the new information will be stored. It saves time by reducing the
amount of time it takes to read the chapter. It creates an interest in what words what the reading is about.
is coming up.
- You may jot down brief notes about what you read.
c) Question
e) Review
- Before you begin reading a section, turn the heading into a question.
- After you have read the entire chapter, look over the notes you made to familiarize important info.
E.g., if the heading is Basic Causes of Stress, your question would be
"What are the basic causes of stress?" - Check your memory by reciting the main points out loud.
-This arouses your curiosity and increases your comprehension. - Then review the main points in your notes, making sure you understand them. Add to your
- It also recalls information you already know. The questions you ask notes from the text, if necessary.
help to make important points stand out as you read. This forces you to
- Always do a review of the chapter after completing your reading. Then do quick reviews
think about what you are reading.
before and after each class. Do longer, more in-depth reviews before exams.
- Don’t wait until exam time to review your textbook. Review once a week all the readings
from that week. Be sure you can summarize the key points. Write them down to further
reinforce learning.