1. Describe the extent of the abdomen:
Origin: Xiphoid Process (medially) & diaphragm (laterally)
Termination: Pelvic Inlet & Pubic Symphisis
2. Boundaries of the Abdominal Cavity
Superiorly: Diaphragm
Inferiorly: Pelvic Inlet
Anteriorly: Muscles (RA, EO, IO, TA), Thoracic Margin
Posteriorly: Lower ribs, Muscles (Psoas M, Quad Lumb)
3. Abdominal Wall Landmarks
Linea Alba: fusion of aponeurosis between 2 Rectus M’s.
Linea Semilunaris: Lateral edge of Rectus Abd. 9th rib to pubic
tubercle.
Umbulicus: Below Linea Alba
Arcuate Line: Posterior layer of rectus sheath
4. Abdominal Planes
Vertical
• R&L Mid-clavicular Lines
Horizontal
• Subcostal/ Transpyloric Planes (10 CC)
• Transumbulical
• Intertubecular (btwn iliac crests & L5).
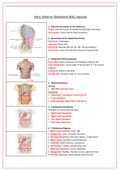
5. 4 Abdominal Quadrants
*Divided by Transumbulical Plane
• Right Upper Quadrant
• Right Lower Quadrant
• Left Upper Quadrant
• Left Lower Quadrant
6. 9 Abdominal Regions
1. Right hypochondrium: Liver, GB
2. Epigastrium: Liver, Stomach, Pancreas
3. Left hypochondrium: Pancreas, Spleen, L Suprarenal,
1 2 3 4. Right lumbar: R Kidney, Ascending colon
5. Umbilical: small intestine, duodenum
4 5 6 6. Left lumbar: L Kidney, descending colon
7. Right iliac (inguinal): Cecum, Appendix
7 8 9 8. Hypogastric: Bladder, Ovaries, Uterus, Sigmoid Colon
9. Left iliac (inguinal): descending & sigmoid colon
,10. Referred pain
Foregut structures: referred to epigastric area
Midgut structures: referred to umbulical region
Hindgut structures: referred to hypogastric area
11. Layers of the Abdominal Wall: SSS Exit
• Skin.
• Subcutaneous fat (Campers fascia)
• Scarpas fascia
• External oblique
• Internal oblique muscle
• Transverse Abdominal muscle
• Transversalis fascia
• Parietal peritoneum
12. High-yield facts on fascia
Campers Fascia: Major Site of Fat Storage
Scarpa’s Fascia: No Fat, fuses with Fascia Lata of Thigh
12. Types of Abdominal Incisions
13. Muscles of Antero-Lateral Abdominal Wall
1)External Oblique Muscle
2)Internal Oblique Muscle
3)Transversalis Muscle
4)Rectus Abdominus
13.1 Actions of External Obliques
Unilaterally: Bends the trunk to the same side AND rotates
the trunk to the opposite side
Bilaterally: Flexes Trunk
, 14. Actions of Internal Obliques
Unilaterally: Bends the trunk to the same side AND rotates
the trunk to the SAME side
Bilaterally: Flexes Trunk
15. Transversalis Muscle
Compresses abdominal contents.
16. Rectus Abdominus: Flexes, tenses trunk
17. Transversalis Fascia
Deepest layer of Abdominopelvic Cavity
- Forms Deep Inguinal Ring & Femoral Sheath
- Deep Ring is formed by the TF pouching out above the
midpoint of the inguinal ligament
- Femoral Sheath is an inferior extension of TF containing
the femoral canal (Artery + Vein)
18. Superficial Arteries of Anterior Abd Wall
• Superficial Epigastric A.
• Br of Femoral A.
19. Deep Arteries of Anterior Abd. Wall
- Superior & Inferior Epigastric Arteries
- Superior: br internal 3thoracic artery
- Inferior: br external iliac artery
Others: Post. Intercostals, lumbar, deep circumflex, iliac A.
20. Deep Veins of Anterior Abd. Wall
1. Superior epigastric,
2. Inferior epigastric
3. Deep circumflex iliac veins
4. Posterior intercostal veins
5. Lumbar veins
21. Superficial Veins of Anterior Abd. Wall
- Above umbilicus: Into lateral thoracic vein
- Paraumbulical veins
- Below umbilicus: Superficial Epigastric
22. Nerve Supply (7)
• FIVE lower intercostal nerves (T7-T11)
• ONE SUBCOSTAL NERVE (T12)
• L1: Ilioinguinal & Illiohypogastric Nerve
• All nerves lie betwn. internal oblique & transversus muscles