Introduction to Anatomy
Presentation by F.K
,A n a tomy I n t rod u cti on
Presentation
Rembrant’s “The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp”: Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human by F.K to the macroscopic.
body, from the microscopic
,I N TRODUCTION
Section One
• Definition of Anatomy
• Subdisciplines
• Anatomical Position
• Common Anatomical Terms
• TERMS OF RELATIONSHIP
• BODY CAVITIES
• Anatomical Planes
Presentation by F.K
,General Study Resources:
Anatomy Resources
• The Institute of Human Anatomy
Instagram • Naz Artonomy
• RevMed
• Osmosis
Apps • Medinaz
• KenHub
• BioMedical
• Anatomyka – 3D Atlas
• Teach Me Anatomy
Presentation by F.K
,W h a t i s A n a to my?
• Anatomy is the study of structures in the body, their
organization and location.
• Physiology is the study of the function of these structures.
• E.g. The heart (structure) is able to pump blood because the
left ventricle contracts to eject blood (function).
Presentation by F.K
,I N TRODUCTION
Anatomy
Anatomy is the study of body structures, their
organization and location . Ana-tomy literally means “to
cut”.
Subdisciplines of anatomy
Systemic anatomy Regional anatomy Surface anatomy Clinical anatomy
Studying how various Studying organs and Superficial/visual/ The practical application
organs & structures structures in a specific topographic anatomy. of anatomy knowledge
work together to region/area. Study of the external to diagnosis and
perform a function. body at rest or in action treatment of
E.g. The Abdomen. with aim of visualizing pathologies.
E.g. The Respiratory landmarks of Incorporates systemic &
System: mouth, nose, structures that lie regional anatomy.
windpipes, lungs. beneath the skin.
E.g. You studied the
heart, how does a heart
attack occur.
Presentation by F.K
,S u b d is ciplines o f a n a to my
Systemic anatomy Regional anatomy Surface anatomy Clinical anatomy
Presentation by F.K
,I N TRODUCTION
Anatomical Position
By convention, anatomical descriptions of
the human body are based on a person
HACK
standing in the “anatomical position”.
• Standing upright (erect) ANTERIOR = VENTRAL
• Facing forward (anterior)
AIR VENT
• Head facing forward
DORSAL = POSTERIOR
• Arms at the side with palms facing
Derererie (Bum, Behind)
anteriorly
• Feet close together facing anteriorly
Presentation by F.K
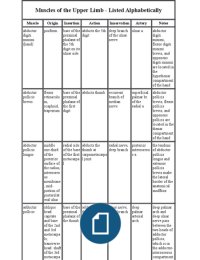
,C o mmon & a n a tomical t e rms
Common Name Anatomical Name Common Name Anatomical Name
Ear Aural Head Cranial
Navel Umbulicus Mouth Oral
Thumb Pollex Nose Nasal
Fingers Digital Cheek Buccal
Arm Brachial Jaw Mandible
Forearm Ante-brachial Neck Cervical
Buttock Gluteal
Ribs Thoracic
Thigh Femoral
Armpit Axillary
Sole Plantar
Palm Palmar
Presentation by F.K
, Directional References
Medial Lateral
Closer to midline Further from the
midline
Superior/Cranial Inferior/Caudal
Closer to head Closer to feet
Superficial Deep/Internal
Closer to the surface Further from
surface.
Anterior Posterior
Infront. Ventral. Behind. Dorsal.
Presentation by F.K