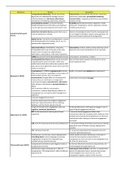
Atmospheric moisture processes
atmospheric moisture - solid, liquid and vapour
- energy is used in the change from one phase to another
● evaporation: heat is absorbed
● heat loss during evaporation passes into the water as latent
heat - vaporisation
● condensation: latent heat locked in water vapour is released
= rise in temperature
● deposition (vapour to ice) = heat is released
● sublimation: heat is absorbed - snow patches disappear
without melting.
Factors affecting evaporation
- occurs when vapour pressure of a water surface exceeds that in
the atmosphere
- vapour pressure: pressure exerted by the water vapour in the
atmosphere - maximum vapour pressure at any point occurs when
the air is saturated
● initial humidity of the air:
❏ if the air is very dry = strong evaporation occurs
❏ is the air is saturated = very little occurs
● supply of heat: the hotter the air, the more evaporation takes
place
● wind strength: air becomes saturated quickly under calm
wind conditions
Factors affecting condensation
occurs when:
- enough water vapour is evaporated into an air mass for it to
become saturated - rare
- when the temperature drops so that dew point (temp. at which air
saturates) is reached - common
such cooling occurs in 3 main ways:
- radiation cooling of the air
, - contact cooling of the air when it rests over a cold surface
- expansive cooling of air when it rises.
Condensation requires a some tiny particles or nucleus onto which
water vapour can attach:
- lower atmosphere - sea salt, dust, pollution particles…
- condensation occurs when the relative humidity is as low as 80%
Other processes
Freezing: liquid ---> solid once the temperature is below 0ºC.
Melting: solid ---> liquid when air temperature is above 0ºC.
Sublimation: solid ---> vapour with no intermediate liquid state
Deposition: vapour ---> ice
Precipitation
all of the deposition of moisture from the atmosphere (solid or liquid
state) - including rain, hail, snow and dew.
1) minute droplets of water rise to the atmosphere - forming clouds -
after they have been condensed from water vapour
2) if droplets coalesce (join), they form larger droplets which
eventually fall as rain
Formation
of droplets
atmospheric moisture - solid, liquid and vapour
- energy is used in the change from one phase to another
● evaporation: heat is absorbed
● heat loss during evaporation passes into the water as latent
heat - vaporisation
● condensation: latent heat locked in water vapour is released
= rise in temperature
● deposition (vapour to ice) = heat is released
● sublimation: heat is absorbed - snow patches disappear
without melting.
Factors affecting evaporation
- occurs when vapour pressure of a water surface exceeds that in
the atmosphere
- vapour pressure: pressure exerted by the water vapour in the
atmosphere - maximum vapour pressure at any point occurs when
the air is saturated
● initial humidity of the air:
❏ if the air is very dry = strong evaporation occurs
❏ is the air is saturated = very little occurs
● supply of heat: the hotter the air, the more evaporation takes
place
● wind strength: air becomes saturated quickly under calm
wind conditions
Factors affecting condensation
occurs when:
- enough water vapour is evaporated into an air mass for it to
become saturated - rare
- when the temperature drops so that dew point (temp. at which air
saturates) is reached - common
such cooling occurs in 3 main ways:
- radiation cooling of the air
, - contact cooling of the air when it rests over a cold surface
- expansive cooling of air when it rises.
Condensation requires a some tiny particles or nucleus onto which
water vapour can attach:
- lower atmosphere - sea salt, dust, pollution particles…
- condensation occurs when the relative humidity is as low as 80%
Other processes
Freezing: liquid ---> solid once the temperature is below 0ºC.
Melting: solid ---> liquid when air temperature is above 0ºC.
Sublimation: solid ---> vapour with no intermediate liquid state
Deposition: vapour ---> ice
Precipitation
all of the deposition of moisture from the atmosphere (solid or liquid
state) - including rain, hail, snow and dew.
1) minute droplets of water rise to the atmosphere - forming clouds -
after they have been condensed from water vapour
2) if droplets coalesce (join), they form larger droplets which
eventually fall as rain
Formation
of droplets