Week 1 Notes: Prokaryotic Transcription
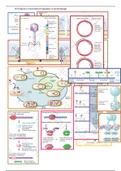
Central dogma
Describes flow of biological information
Introduction
Transcription is 5’ to 3’ on template that is 3’ to 5’
Coding strand (non template): DNA strand w/same seq as mRNA (U instead of T) and is related by genetic
code to the prot seq it represents
RNA pol: enzyme that synthesises RNA using DNA template
Transcription unit
Promoter: region of DNA where RNA pol binds to initiate transcription
Startpoint: DNA position corresponding to first base incorporated into RNA (begins at +1)
Terminator: DNA sequence that causes RNA pol to terminate transcription
Transcription unit: DNA sequence b/w sites of initiation and termination by RNA pol
o May include more than one gene
Prokaryotic transcription Eukaryotic transcription
Transcription occurs by base pairing in a ‘bubble’ of unpaired DNA
RNA pol separates both strands in a transient (temporary) ‘bubble’
o Uses one strand as template for direct synthesis of complementary RNA seq
‘Bubble’ length is 12-14 bp ; RNA-DNA hybrid length is 8-9 bp
RNA polymerisation
3’-OH group of the last ribonucleotide added to the chain reacts with an incoming ribonucleotide 5’
triphosphate
rNTP: ribonucleoside w/3 phosphates, building blocks of RNA synthesis & primers in DNA replication
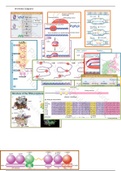
Transcription: 3 stages
Initiation:
o RNA pol binds to promoter on DNA to form closed complex
Central dogma
Describes flow of biological information
Introduction
Transcription is 5’ to 3’ on template that is 3’ to 5’
Coding strand (non template): DNA strand w/same seq as mRNA (U instead of T) and is related by genetic
code to the prot seq it represents
RNA pol: enzyme that synthesises RNA using DNA template
Transcription unit
Promoter: region of DNA where RNA pol binds to initiate transcription
Startpoint: DNA position corresponding to first base incorporated into RNA (begins at +1)
Terminator: DNA sequence that causes RNA pol to terminate transcription
Transcription unit: DNA sequence b/w sites of initiation and termination by RNA pol
o May include more than one gene
Prokaryotic transcription Eukaryotic transcription
Transcription occurs by base pairing in a ‘bubble’ of unpaired DNA
RNA pol separates both strands in a transient (temporary) ‘bubble’
o Uses one strand as template for direct synthesis of complementary RNA seq
‘Bubble’ length is 12-14 bp ; RNA-DNA hybrid length is 8-9 bp
RNA polymerisation
3’-OH group of the last ribonucleotide added to the chain reacts with an incoming ribonucleotide 5’
triphosphate
rNTP: ribonucleoside w/3 phosphates, building blocks of RNA synthesis & primers in DNA replication
Transcription: 3 stages
Initiation:
o RNA pol binds to promoter on DNA to form closed complex