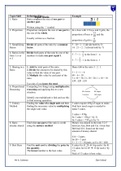
Components of pagan temples - Answers Stylobate: The uppermost step of the temple platform
upon which the columns rest.
Peristyle: A colonnade or row of columns surrounding a building or an open space.
Columns: Vertical architectural elements that typically consist of a base, shaft, and capital, used
to support structures or as decoration.
Capital: The topmost part of a column, serving as a transition between the shaft and the load it
supports.
Cella: The central chamber of a Greek or Roman temple, where the cult statue usually stood.
Entablature: The horizontal structure supported by the columns, consisting of the architrave,
frieze, and cornice.
Architrave: The lowest part of the entablature, resting directly on the columns.
Frieze: The middle part of the entablature, often decorated with sculpture or relief.
Triglyphs: Architectural elements in the frieze of a Doric entablature, typically consisting of three
vertical grooves.
Metopes: The spaces between triglyphs in a Doric frieze, often decorated with relief sculpture.
Cornice: The uppermost part of the entablature, projecting outward and often elaborately
decorated.
, Pediment: The triangular space at the end of a building, formed by the sloping ends of the roof
and the cornice, often decorated with sculpture or relief.
Greek orders (Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian) - Answers Doric: The Doric order is the simplest and
oldest of the classical orders. Doric columns are typically stout and sturdy, with no base and a
simple capital consisting of a rounded molding called an echinus and a square slab called an
abacus. Doric columns are often fluted and have a plain, undecorated shaft. The entablature in
the Doric order is characterized by a frieze with alternating triglyphs and metopes.
Ionic: The Ionic order is more ornate and slender than the Doric order. Ionic columns are
typically taller and have a base, a fluted shaft, and a capital with volutes (scroll-like ornaments)
on either side. The entablature in the Ionic order usually has a continuous frieze without
triglyphs, and the cornice may be more elaborate than in the Doric order.
Corinthian: The Corinthian order is the most ornate and elaborate of the classical orders.
Corinthian columns are similar to Ionic columns but feature capitals adorned with acanthus
leaves and small volutes. The Corinthian order is often associated with luxury and grandeur and
is commonly used in more decorative and prestigious buildings.
Contrapposto - Answers The disposition of the human figure in which the hips and legs turned
in opposition to the shoulders and chest, creating a counter-positioning of the body.
Acropolis - Answers Greek for "high city". The chief temples of the city were located here.
Entasis - Answers The convex profile (an apparent swelling) in the shaft of a column.
Caryatid - Answers a female figure that functions as a supporting column
Lost-wax bronze casting - Answers a bronze-casting method in which a figure is modeled in wax
and covered with clay; the whole is fired, melting away the wax and hardening the clay, which
then becomes a mold for molten metal
Republic - Answers senate- latin senatus, council of elders
consuls- in the Roman Republic, two chief magistrates
Patrician - Answers Roman freeborn landowner
Plebeian - Answers The Roman social class that included small farmers, merchants, and freed
slaves.