Correct Answers/ PRITE - Psychiatry Resident In-Training
Examination Practice Test Bank Newest 2025-2026
A 32-year-old patient with schizophrenia, stable on olanzapine, gained over 20
pounds in one year (BMI now at 31 kg/m) and has elevated fasting glucose and
triglycerides. Which of the following is the best supported treatment for the
metabolic side effects?
A. Insulin
B. Orlistat
C. Metformin
D. Gemfibrozil
E. Atorvastatin
C. Metformin
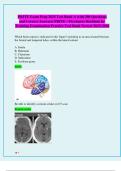
A patient presents with progressive, worsening movements of the limbs and face.
Which of the following diagnoses is best supported by this MRI scan? (shows
atrophy of caudate nucleus and putamen with concomitant enlargement of the
frontal horns of the lateral ventricles)
A. Wilson disease
B. Friedrich ataxia
C. Parkinson disease
D. Huntington disease
E. Spongiform encephalopathy
D. Huntington disease
https://radiopaedia.org/articles/huntington-disease?lang=us
pg. 1
,A patient with Alzheimer disease is admitted due to a displaced fracture of the
radius, caused by a ground level fall at home. The team is recommending surgery,
however the patient is refusing. Which of the following is the most appropriate
next step?
A. Watchful waiting
B. Assess capacity to refuse
C. Contact adult protective services
D. Seek a surrogate decision maker
E. Recommend proceeding with surgery
B. Assess capacity to refuse
According to Kohut, which of the following traits is normal in children and a
significant aspect of healthy personality development?
A. Altruism
B. Likeability
C. Narcissism
D. Persistence
E. Assertiveness
C. Narcissism
PMID: 20428310
Which of the following behavioral techniques should be utilized in the de-
escalation of an agitated patient?
A. Maintain constant eye contact
pg. 2
,B. Acknowledge the patient's frustrations
C. Speak louder than the patient as a show of force
D. Stand while the patient sits to allow for a quicker exit
E. Make gentle physical contact to demonstrate empathy
B. Acknowledge the patient's frustrations
During the neurological examination, a 59-year-old patient is asked to slap the
palm of his hand on his knee, alternating with the back of his hand, in rapid
succession. He performs this maneuver with difficulty, often clumsily hitting the
side of his hand at an irregular tempo. Which of the following describes the
abnormality demonstrated with this maneuver?
A. Ballism
B. Chorea
C. Apraxia
D. Focalmyoclonus
E. Dysdiadochokinesia
E. Dysdiadochokinesia
Prolonged stimulation of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptors is
hypothesized to result in neuronal death due to:
A. Excessive calcium influx resulting in mitochondrial caspase activation
B. Reduced sodium influx resulting in relative hypotonicity and cellular necrosis
C. Excessive chloride influx resulting in relative hypertonicity and cellular necrosis
D. Increased ATP production resulting in collapse of sodium and potassium
gradients
E. Increased production of beta-amyloid resulting in disruption of the cellular
cytoskeleton
A. Excessive calcium influx resulting in mitochondrial caspase activation
Opening an NMDA receptor requires:
AMPA to depolarize the membrane to dislodge NMDA Mg2+ blockade, 2
molecules of glycine (co-agonist) to bind to NMDA NR1 subunit, 2 molecules of
Glu (ligand) to bind to NMDA NR2 subunit. The result is influx of Ca2+, leading
to a cascade involving protein kinases and gene transcription. Antagonists include
PCP, ketamine, amantadine, and memantine.
pg. 3
, The parent of a 43-year-old patient died 5 years ago from pancreatic cancer. Four
years ago, the patient noticed occasionally feeling uncomfortably full after eating
large, fatty meals, and began fearing that this was an early sign of pancreatic
cancer. The patient acknowledges that this is unlikely, but feels the need to
frequently weigh himself to be reassured that he is not losing weight. The patient
had previously scheduled annual physicals, but now avoids seeing the doctor due
to the fear of being diagnosed with cancer. There are no other psychiatric
symptoms. Which of the following is this patient's most likely diagnosis?
A. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
B. Delusional disorder, somatic type
C. Somatic symptom disorder
D. Illness anxiety disorder
E. Conversion disorder
D. Illness anxiety disorder
During an intensive psychotherapy session, a patient becomes increasingly
annoyed at the therapist and blurts out, "You must really hate me." This is most
accurately understood as which of the following defense mechanisms?
A. Projection
B. Resistance
C. Displacement
D. Reaction formation
E. Projective identification
A. Projection
A four-year-old child has been raised in a series of foster homes. The child
minimally smiles during interactions with a responsive caregiver. When upset, the
child does not seek comfort from the caregiver. The child has episodes of
unexplained irritability and sadness. Which of the following is most likely
diagnosis for this child?
A. Selective mutism
B. Acute stress disorder
C. Separation anxiety disorder
pg. 4