Dr John Connelly
Cell Motility
• Motor and structural proteins = motile system
• Cytoskeleton = scaffold for mechanoenzymes
Eukaryotic Motility Systems
1. Motor proteins and microtubules
a. Axon transport neurons
b. Sliding of microtubules in flagella
2. Actin and myosin motor proteins
a. Muscle contractions
Proteins
• Dynein – inbound to +
o Heavy, intermediate and light chains
o Also has ATP
• Kinesin – outbound to -
o Globular head region attaches to microtubules
o Coiled helical region
o Light chain region that attaches to vesicles and organelles
o “Walks” as a dimer
o Uses ATP hydrolysis for energy
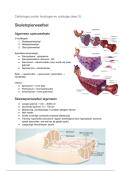
Cilia and Flagella
• Cilia
o 2-10µm long in eukaryotes
o Oar-like beating pattern
• Flagella
o Same diameter as cilia, but 10-200µm long
o Moves cell through fluid
o Only 1 or 2 per cell
o Propagated bending motion
• Axoneme
o Shared structure – 9x2
o 9 outer doublets and 2 inner singlet microtubules
o Separated by 9 dynein
• Sliding microtubules model
o Provided by ATP hydrolysis of dynein
Actin-Based Motility
• Myosins are ATP dependent motors – 24 types
• Tetramer – 2 heavy, 2 light
• Muscle contraction, movement, endocytosis
• 6 classes