Multimodale communicatie - hoorcollege aantekeningen
11 juni
week 1 hoorcollege
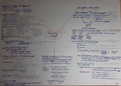
Multimodality is a broader approach to communication that goes beyond language and verbal
texts and also involves nonlinguistic resources (e.g. images, videos, sounds). When, in studies
of human communication, we often tend to distinguish between various forms of expression, we
do so because we are influenced by the traditional division into scientific fields; linguistics,
media studies, art history etc. in the real world, and in real communication, the forms of
expression are not separated in the same manner. They always work together in a complex,
multimodal interplay.
Multimodal turn…?
- Growing orientation to multimodality as a cultural phenomenon
- Emergence of ‘super-media’ and media convergence
- Particular focus in areas of literacy and pedagogy
- Implementations in curricula and guidelines
→ willingness and need to examine combinations of expressive resources explicitly and
systematically in and across all disciplines
Need
Find out more about the fundamental properties of multimodal meaning making:
- Meaning combination.multiplication
- Semiotic modes
- Communicative situations and media
Challenge:
- Huge diversity of multimodal phenomena
- New media and technologies produce them in/for every area of communication
- Various research questions and approaches from various disciplines
- Little use of regularities/shared sources
Challenge accepted
- Useful statements and analyses of multimodal forms and styles
- With a deeper understanding of how multimodality operates on all levels of
communication
werkgroep 1
Why might it be beneficial to know about multimodality? → a company can benefit while
creating a poster, because you might know what the customer likes.
What are some typical cases of multimodality? → Examples are TikTok videos, Instagram photo
with a caption, advertisements, text messages etc.
1
,hoofdstuk 1
Multimodality refers to communication involving multiple modes (e.g., language, image,
gesture, layout, sound). It's the norm, not the exception, in modern communication (TV, social
media, education, games, face-to-face interaction).
Why it matters:
- Traditional disciplines (linguistics, art, film, etc.) study communication in isolation (one
mode at a time)
- This limits understanding of how modes work together to create meaning
- Multimodal analysis helps us interpret complex, layered communication more accurately.
- Multimodal Turn: A shift in awareness across academia and society toward recognizing
multimodality as essential.
- Mode: A socially and culturally shaped resource for meaning-making (e.g., text, image,
sound, gesture). But the concept lacks a universally agreed definition.
- Meaning Multiplication: Multimodal combinations produce more meaning than
individual modes alone.
- Interdependence: Modes affect each other’s meaning—meaning isn't fixed or isolated.
- Multimodal Ensembles: The total combination of interacting modes in a communicative
event.
Challenges in analysis:
- No clear or consistent method for identifying or analyzing modes.
- Current methods often depend on the analyst’s disciplinary background.
- Risk of oversimplifying or misinterpreting complex multimodal texts.
video 2
Problem space multimodality
1. Materiality (and the senses)
2. Language
3. Semiotics
4. Society, culture, media
1. Materiality
- Physical events or objects in the world
- Acts of interpretation
physical events interpretation
sound acoustic space, distance, etc
music & sound design
vision (light to the eye)
2
, visuality (All meaning making processes)
compositionality
visual associations
resemblance
visual propositions
2. Language
- Face-to-face conversation (stress, rhythm, intonation, body movement etc)
- HCI: human computer interaction (how modes can be combined in this service of
communication)
- Literary studies (problems with new media for example)
- Linguistics
- Grammar
- SFL: systemic functional linguistics
- Discourse analysis
3. Semiotics
Discipline that considers how meaning can be made through the use and exchange of
meaning-baring vehicles. Strongly connected to linguistics. (Verbal signs and expressive forms)
- Ferdinand de Saussure > focuses on verbal signs → signifier & signified
- Definitions of the ‘sign and processes of sign-making’
- Charles Sanders Peirce > three way model → interpretant, object, sign/representamen
- icon, index, symbol
- Principle of abduction (besides induction & deduction); hypotheses are built on
certain information available, but these hypotheses might be proven wrong when
new information becomes available.
- Abduction can be used to relate text and
4. Society, culture, media
- Communicative actions (questions focus on nature of communication in society, for
example)
- Mediatization
- To analyze the interrelation between changes in media and communications on
the one hand, and changes in culture and society on the other.
- Media need to be seen as particular ‘bundles’ of semiotic modes. Whereas the specific
media offer an interface to considerations of society, institutions, distribution and
technology, the ‘modes’ within any specific media describe just what they are capable of
doing in terms of meaning-making.
3
11 juni
week 1 hoorcollege
Multimodality is a broader approach to communication that goes beyond language and verbal
texts and also involves nonlinguistic resources (e.g. images, videos, sounds). When, in studies
of human communication, we often tend to distinguish between various forms of expression, we
do so because we are influenced by the traditional division into scientific fields; linguistics,
media studies, art history etc. in the real world, and in real communication, the forms of
expression are not separated in the same manner. They always work together in a complex,
multimodal interplay.
Multimodal turn…?
- Growing orientation to multimodality as a cultural phenomenon
- Emergence of ‘super-media’ and media convergence
- Particular focus in areas of literacy and pedagogy
- Implementations in curricula and guidelines
→ willingness and need to examine combinations of expressive resources explicitly and
systematically in and across all disciplines
Need
Find out more about the fundamental properties of multimodal meaning making:
- Meaning combination.multiplication
- Semiotic modes
- Communicative situations and media
Challenge:
- Huge diversity of multimodal phenomena
- New media and technologies produce them in/for every area of communication
- Various research questions and approaches from various disciplines
- Little use of regularities/shared sources
Challenge accepted
- Useful statements and analyses of multimodal forms and styles
- With a deeper understanding of how multimodality operates on all levels of
communication
werkgroep 1
Why might it be beneficial to know about multimodality? → a company can benefit while
creating a poster, because you might know what the customer likes.
What are some typical cases of multimodality? → Examples are TikTok videos, Instagram photo
with a caption, advertisements, text messages etc.
1
,hoofdstuk 1
Multimodality refers to communication involving multiple modes (e.g., language, image,
gesture, layout, sound). It's the norm, not the exception, in modern communication (TV, social
media, education, games, face-to-face interaction).
Why it matters:
- Traditional disciplines (linguistics, art, film, etc.) study communication in isolation (one
mode at a time)
- This limits understanding of how modes work together to create meaning
- Multimodal analysis helps us interpret complex, layered communication more accurately.
- Multimodal Turn: A shift in awareness across academia and society toward recognizing
multimodality as essential.
- Mode: A socially and culturally shaped resource for meaning-making (e.g., text, image,
sound, gesture). But the concept lacks a universally agreed definition.
- Meaning Multiplication: Multimodal combinations produce more meaning than
individual modes alone.
- Interdependence: Modes affect each other’s meaning—meaning isn't fixed or isolated.
- Multimodal Ensembles: The total combination of interacting modes in a communicative
event.
Challenges in analysis:
- No clear or consistent method for identifying or analyzing modes.
- Current methods often depend on the analyst’s disciplinary background.
- Risk of oversimplifying or misinterpreting complex multimodal texts.
video 2
Problem space multimodality
1. Materiality (and the senses)
2. Language
3. Semiotics
4. Society, culture, media
1. Materiality
- Physical events or objects in the world
- Acts of interpretation
physical events interpretation
sound acoustic space, distance, etc
music & sound design
vision (light to the eye)
2
, visuality (All meaning making processes)
compositionality
visual associations
resemblance
visual propositions
2. Language
- Face-to-face conversation (stress, rhythm, intonation, body movement etc)
- HCI: human computer interaction (how modes can be combined in this service of
communication)
- Literary studies (problems with new media for example)
- Linguistics
- Grammar
- SFL: systemic functional linguistics
- Discourse analysis
3. Semiotics
Discipline that considers how meaning can be made through the use and exchange of
meaning-baring vehicles. Strongly connected to linguistics. (Verbal signs and expressive forms)
- Ferdinand de Saussure > focuses on verbal signs → signifier & signified
- Definitions of the ‘sign and processes of sign-making’
- Charles Sanders Peirce > three way model → interpretant, object, sign/representamen
- icon, index, symbol
- Principle of abduction (besides induction & deduction); hypotheses are built on
certain information available, but these hypotheses might be proven wrong when
new information becomes available.
- Abduction can be used to relate text and
4. Society, culture, media
- Communicative actions (questions focus on nature of communication in society, for
example)
- Mediatization
- To analyze the interrelation between changes in media and communications on
the one hand, and changes in culture and society on the other.
- Media need to be seen as particular ‘bundles’ of semiotic modes. Whereas the specific
media offer an interface to considerations of society, institutions, distribution and
technology, the ‘modes’ within any specific media describe just what they are capable of
doing in terms of meaning-making.
3