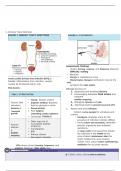
FIGURE 1. URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS FIGURE 2. CYSTOSCOPY
Assessment findings:
Urinary burning, urgency, and frequency (dysuria)
Difficulty voiding
Nocturia
Cloudy or malodorous urine
Acute cystitis (urinary tract infection [UTI]) is
Mental status changes (confusion) may be the
bladder inflammation from infection, usually
only
caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli).
symptom for older adults.
Risk factors:
UTI care focuses on:
1. Assessing and treating infection
TABLE 1. UTI RISK FACTORS 2. Encouraging adequate fluid intake and
frequent
Female: Shorter urethra bladder emptying
Factors that Diabetes mellitus: Bacteria 3. Managing dysuria and pain
introduce feed on glucose in urine. 4. Teaching client to prevent recurrent UTIs
bacteria or Sexual activity 1. Assess and treat infection:
bacterial Poor hygiene
Collect a urine sample for urinalysis and
growth Indwelling urinary catheters culture:
Cystoscopy (FIGURE 2) Urinalysis: Analyzes urine for the
presence of infection (nitrate, WBCs)
Older age:risk of
Urine culture and sensitivity: Identifies
Factors incomplete bladder
emptying specific organisms and antibiotic
affectin sensitivity
Constipation
g A clean-catch urine specimen should
BPH
bladder be collected in the middle of the
Kidney stones
emptying urine stream (midstream) after the
Neurogenic bladder
client initiates the urine stream.
Collect urine culture before administering
UTIs cause urinary burning, frequency, and antibiotics for accurate results.
urgency. However, older adults may
experience confusion as the only symptom.
@ Collect urine culture before antibiotic
, administration. specimen, pass the specimen container into
When collecting a clean catch urine the urine stream
This study source was downloaded by 100000892998434 from CourseHero.com on 11-18-2024a1f0t:e41r:1t9hGeMcTlie-0n6t:0i0nitiates the urine
stream.
Table of Contents:
Urinary Tract Infection 3. Medications
Pyelonephritis
Urinary Tract Infections