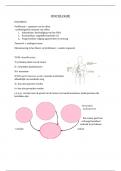
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
• Biological and physiological needs
• Safety needs
• Love and belongingness needs
• Esteem needs
• Cognitive needs
• Aesthetic needs
• Self-actualisation
• Transcendence needs
Basic human needs need to be satisfied before moving onto satisfy higher needs
Needs need to be fulfilled according to the hierarchy.
Alderfer's ERG theory
• Existence needs- physiological and safety needs
• Relatedness needs- social and self-esteem needs
• Growth needs- self-development and advancement
Not hierarchical
People can be motivated by needs from more than one level at a time
Relative importance of needs may change throughout our lives.
McClelland's theory of achievement motivation
• Need for achievement-success, get things done
• Need for power-influence, control over others
• Need for affiliation- maintain social relationships
TAT- thematic apperception test a series of ambiguous images which an individual is asked to interpret
measures the need for achievement
,COGNITIVE THEORIES-9.1
Goal setting theory-Locke and Latham
• Clarity
• Challenge
• Complexity
• Commitment
• Feedback
Setting specific goals produces a high level of performance than setting vague goals.
Specific goals harder to achieve, make individual work harder.
Feedback needs to be positive and constructive.
Expectancy theory- vroom
• Expectancy- perception of how much effort relates to performance as well as workers
confidence in their abilities
• Instrumentality-perception of how much effort will be rewarded and whether they believe they
will be rewarded
• Valence-perception of the strength or size of reward and how much they value it
Worker's performance can be influenced by these factors including knowledge, skills, experience ,
individual characteristics
If the favourable performance is rewarded the reward satisfies a need.
Equity theory- Adams
• Workers expect things to be fair
• Pay, status and recognition should equate to how much work they put in
• If workers perceive other being treated better than them the perceived inequality will lead to
decreased motivation
• Inputs- skills, qualifications, energy, enthusiasm and effort
• Outputs-pay, recognition, involvement
• Inequality- under payment over payment
, MOTIVATORS AT WORK-9.1
Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation
• Intrinsic motivators- enjoyment, sense of satisfaction ,achievement
• Extrinsic motivators- money, promotions, bonuses
Reward systems
• Rewards- pay, bonuses, profit sharing, performance related pay. Gives workers a stronger sense
of belonging and increase motivation
• Research conducted in UK show no relationship between size of bonus and performance
• De Waal and Jansen- orgs with high inequalities had high staff turnover.
Monetary and non-monetary rewards.
• Non- monetary rewards- praise respect, recognition through employee of the month schemes,
empowerment, sense of belonging.
These come from other people and can be extremely motivating.
makes you feel good about yourself.
Recognition can produce a sense of empowerment.
Schemes can highlight desired behaviours and create role models, very low costs.
staff turnover can be positively affected. Increases satisfaction ratings
builds positive relationships between manager and workers