💧
Module 24: Urinary System
Created @November 30, 2022 2:26 PM
Reviewed
Status Not started
TOPICS COVERED
Understand homeostatic control in the body
KEY TERM
Plasma:
Leukocytes:
Platelets:
Antidiuretic hormone:
Hypertonic: a relatively low water and a high salt concentration.
Hypotonic: a relatively high water and a low salt concentration.
NOTES
Urine Production
Composition of Blood Composition of Urine
55% of human blood comprises: Urine is a yellowish liquid with
a distinctive smell.
Plasma, which is made up of water.
Urine consists of:
Dissolved gases.
Module 24: Urinary System 1
, Useful substances including Water – the main component of
glucose, mineral salts, amino acids urine which acts as a solvent
and fatty acids. for many substances.
Dissolved waste which Inorganic salts – including
includes urea, uric acid, creatinine chloride, sulphate and phosphate
and large proteins. ions of calcium, sodium and
magnesium.
45% of total blood is comprised
of erythrocytes (red blood cells) Metabolic wastes – including urea,
<1% consists of uric acid and creatinine.
leukocytes (white blood cells) Foreign substances – including
flavourants, colourants and
platelets preservatives that are taken in with
food, as well as drugs.
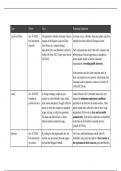
Homeostatic Regulation By Kidneys
The kidney is involved in three homeostatic mechanisms:
1. Regulation of pH of the blood – an integral component of urine formation.
2. Regulation of water levels (osmoregulation).
3. Regulation of salt levels in the blood.
Regulation of water levels:
The antidiuretics hormone (ADH) is the hormone that controls the permeability of
the walls in the distal convoluted and the collecting duct and controls how much
water is reabsorbed
As blood flows through our brain, the hypothalamus detects whether there is too
little or too much water in our blood.
Regulation of salt levels
Our kidneys work together with the adrenal glands to control the concentration
of Na+ in our blood.
This control occurs via the hormone aldosterone, which is secreted by the
adrenal glands.
Control of salt Hypertonic:
Module 24: Urinary System 2
Module 24: Urinary System
Created @November 30, 2022 2:26 PM
Reviewed
Status Not started
TOPICS COVERED
Understand homeostatic control in the body
KEY TERM
Plasma:
Leukocytes:
Platelets:
Antidiuretic hormone:
Hypertonic: a relatively low water and a high salt concentration.
Hypotonic: a relatively high water and a low salt concentration.
NOTES
Urine Production
Composition of Blood Composition of Urine
55% of human blood comprises: Urine is a yellowish liquid with
a distinctive smell.
Plasma, which is made up of water.
Urine consists of:
Dissolved gases.
Module 24: Urinary System 1
, Useful substances including Water – the main component of
glucose, mineral salts, amino acids urine which acts as a solvent
and fatty acids. for many substances.
Dissolved waste which Inorganic salts – including
includes urea, uric acid, creatinine chloride, sulphate and phosphate
and large proteins. ions of calcium, sodium and
magnesium.
45% of total blood is comprised
of erythrocytes (red blood cells) Metabolic wastes – including urea,
<1% consists of uric acid and creatinine.
leukocytes (white blood cells) Foreign substances – including
flavourants, colourants and
platelets preservatives that are taken in with
food, as well as drugs.
Homeostatic Regulation By Kidneys
The kidney is involved in three homeostatic mechanisms:
1. Regulation of pH of the blood – an integral component of urine formation.
2. Regulation of water levels (osmoregulation).
3. Regulation of salt levels in the blood.
Regulation of water levels:
The antidiuretics hormone (ADH) is the hormone that controls the permeability of
the walls in the distal convoluted and the collecting duct and controls how much
water is reabsorbed
As blood flows through our brain, the hypothalamus detects whether there is too
little or too much water in our blood.
Regulation of salt levels
Our kidneys work together with the adrenal glands to control the concentration
of Na+ in our blood.
This control occurs via the hormone aldosterone, which is secreted by the
adrenal glands.
Control of salt Hypertonic:
Module 24: Urinary System 2