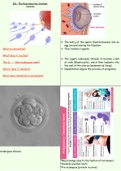
Conception
The entry of the sperm (Spermatozoan) into an
egg (oocyte) during fertilisation
What is conception? This creates a zygote
What does it creates?
The zygote undergoes division to become a ball
The Z___ then undergoes what? of cells (Blastocysts), which then implants into
the wall of the uterus (endometrial lining)
Where does it implants? Implantation begins the process of pregnancy
What does implantation symbolises?
Undergoes mitosis
*Mood swings (due to fluctuation of hormones)
*Oedema (swollen feet)
*Pre-eclampsia (protein in urine)
, B11: The Reproductive System
Development of the Placenta
Vascular (has a lot of blood vessels) structure that
develops after implantation
What is placenta? To supply the foetus with nutrients and oxygen, and
remove waste products such as urea and carbon dioxide
What is the role of the placenta?
The placental chorion produces the hormone hCG
(Human chorionic gonadotropin) that is detected by the
What does the placental chorion produce?
pregnancy test.
What is the function of it? the hCG's function is to stimulate the corpus luteum to
produce more progesterone to maintain pregnancy
B11: The Reproductive System
Prenatal development
Week 12
Week 4:
Fingernails are developed; most
Heart starts to beat; basic placenta
organs and structures are fully
and umbilical cord are working
formed
Size: poppy seed
Size: Lemon
Length: 1mm
Length: 5.4 cm
Week 8 Week 16:
The heart has four chambers and Skeleton and nerves continue to
blood is circulating; toe buds develop develop; can hiccup and suck thumb
Size: grape Size: avocado
Length: 1.6 cm Length: 11.6 cm
,B11: The Reproductive System
Prenatal development
Week 20 Week 28
Skin gets thicker and develops Foetus has eyebrows and eye
different layers lashes; brain development
Size: Coconut increases
Length: 25.6 cm Size: lettuce
Length: 37.6 cm
Week 24: Week 32
Foetus can tell if its upside down; The foetus starts to inhale
legally a foetus can be aborted up amniotic fluid to exercise its lungs
to this point Size: turnip
Size: Swede Length: 42.4 cm
Length: 30 cm
Week 36
Rapid weight gain
Size: papaya
Length: 47.4 cm
Week 40
Baby is ready to be born
Size: pumpkin
Length: 51.2 cm
, B11: The Reproductive System
The stages and significant developments during growth
through the trimesters
·The embryo grows rapidly, and the replicated cells separate into
tissues and organs
·The whole embryo becomes enclosed in a fluid-filled sac (amnion)
·The amnion and amniotic fluid cushion the embryo and protect it
·The chorion is concerned with the transport of oxygen and
nutrients from the mother’s blood to the foetal blood by the
chorionic villi and toward the end of this trimester the placenta
(which lasts for the remainder of the pregnancy is formed from
the villi)
·The foetus is attached to the placenta by the umbilical cord,
which links to the mother.
Outline what happens in the First trimester ·Although the mother’s blood never mixes with the foetal blood
the two lie very close together and materials (dissolved oxygen,
glucose, amino acids and lipids products) pass between them by
diffusion (from the mother to the foetus) and carbon dioxide,
water and urea pass from the foetus to the mother’s blood to be
eliminated by her urine and expired air
The placenta should be fully formed, anchoring the foetus in th
uterus and producing hormones to maintain the pregnancy
The mother starts to feel the foetus moving at around 18-2
weeks (Quickening) and hair, eyebrows, lashes, finger, toenail
start to appear
Organs are formed and working
From week 20 the foetal heartbeat can be heard with
Outline what happens in the Second trimester stethoscope, although it has been beating from 5-6 (which can b
seen on an ultrasound scan)
What does quickening mean
When the pregnant woman first feels the foetus move