Urinary functions and functional anatomy
Urinary functions
• Aim: homeostasis in body fluids
• Regulation of ECF volume, osmolarity and electrolyte balance by handling water and
electrolytes
• Regulation of acid-base balance by controlling H+ and HCO3- levels
• Excretion of metabolic end-products and foreign substances like urea, uric acid and
creatinine
• Retaining of adequate amounts of essential substances
,
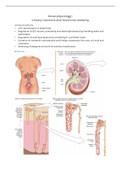
,Blood supply of the superficial and juxtamedullary nephrons
The renal corpuscle (body of Malphigi)
Mesangial cells
• Structural support for
capillaries
• Secrete extracellular
matrix
• Phagocytic activity
• Left: micrograph
showing podocyte foot
, processes around glomerular capillaries
• Right: fenestrations (small holes ±700 Å) of endothelial cells from inside of glomerular
capillary
Mechanisms of kidney function