BIOL 1108
BIOL 1108: Principles of Biology II Exam 2
(Latest 2026/ 2027 Update) Review| 100%
Verified Questions & Answer| Grade A.
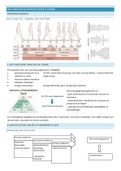
1.phylogeny: shows the evolutionary history and relatedness of a group of
organisms
2.phylogenetic tree: a branching diagram representing a hypothesis about the
evolutionary relationship among a group of organisms
3.reading a phylogenetic tree: time runs from the base of the tree and to the
tip of the branches, branches split at forks called nodes which represents the
most recent common ancestor of two descendant groups 4. construction of
phylogenetic tree: trees are constructed by comparing the anatomy,
physiology, and molecular features of each group. trees are a hypothesis
about the evolutionary history of a species
5. sister groups: two groups that are more closely related to each other than
either one is to anything else on the tree
BIOL 1108
, 2
BIOL 1108
6. taxa: group or level of organization into which organisms are classified
7. taxonomy: the field that provides formal means to naming groups
8. monophyletic group: a group in which all members share a single common
ancestor that is not shared with any other species or groups of species
9. paraphyletic group: includes some, but not all, of the descendants of a
common ancestor
10. polyphyletic group: members share traits evolved independently by
convergent evolution, not through a common ancestor
11. convergent evolution: when two species that are not closely related
end up looking or acting similar because they live in similar environments
and/or face similar environmental struggles
12. taxonomy classifications: summarizes existing scientific evidence on
relatedness
13. character: are the morphological, physiological, or molecular features
that make up the organism
14. character states: observed conditions, characters can be present or
absent
BIOL 1108
, 3
BIOL 1108
15. homology: characters that are similar in different species because of
descent from a common ancestor but may serve different functions
16. analogy: characters that are similar in different species but evolved
independently in different groups as adaptions to their environment
17. synapomorphies: shared derived characters that arose from a common
ancestor
18. derived character: evolutionary innovation
19. niche: the combination of species' physical habitat and its ecological roll
20. fundamental niche: the full range of climate conditions and food
resources that permit the individuals in a species to live
21. realized niche: the actual range of habitats occupied by a species,
affected by interactions with other species (such as competition and
predation)
22 habitats: where an organism lives
23. phylogenetic niche conservatism: species tend to keep living in the
same types of environments
BIOL 1108