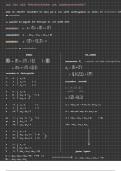
Lecture 1
- An MRS in a firm is as the human brain in our body
- Decision-facilitating, decision-influencing & coordination-facilitating function
of MRS
- Diagnostic & interactive use of MRS
,- The gap/principal-agent problem
A situation in which one individual (the agent or employee) acts on behalf of another
individual (the principal or business man) and is supposed to advance the principal’s goals
(through providing effort). However, often the agent and principal have opposing interests.
This causes problems:
1) Effort of the agent (‘a’) is unobservable because
a) Continuous monitoring of the agent is too costly
b) The principal has not enough knowledge to judge the agent’s effort
2) Risk-averse agents combined with a noisy signal (‘x’) of the agent’s effort
3) The signal (‘x’) can be manipulated by the agent
- Imperfect information in MRS
An MRS provides information about the employee’s effort. The obtained accuracy of
information contained in the MRS is the outcome of a cost-benefit tradeoff. Because
managers need to keep the financial constraints, contextual factors and bounded rationality
in mind → so there is imperfect information, and the true effort of the agent is
unobservable.
- Conceptualization of the employee
In economic models employees are often assumed to be lazy, only extrinsically motivated,
selfish and rational. In real-life employees are also lazy and selfish but employees also like
their job, have (some) intrinsic motivation for their job and do not always go for the
best-paying option. They are also sometimes biased.
Lecture 2
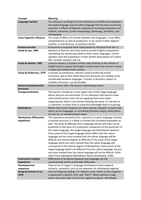
- 3-legged stool as an analogy for the complementarity between different
elements one has to focus on when implementing a strategy
, The 3-legged stool is a metaphor for the complementarity between different elements of
strategy implementation/management control. If you want to implement a strategy, you
need to consider the organizational design, reporting system, performance evaluation, and
soft control.
However, it is also important that you consider the links between these different elements,
implying that if you change one element you also need to consider whether the other
elements need to be changed. In case you do not do this, the investments in improving the
performance evaluation system, for instance, is unlikely to realize its expected return on
investment.
- Different elements of the 3-legged stool (organizational design, reporting
systems, performance evaluation and soft controls)
- Reporting system: Deals with all the information that is collected and distributed in the
firm
- Performance evaluation: Refers to how performance of individuals, teams and
departments is measured and rewarded in organizations → KPIs (financial/non-financial,
subjectivity)
- Organizational design: The design of the organization. Two important decisions: (1) the
structure of the organization (by market, function etc.), and (2) delegation
- Soft controls: culture, leadership and social norms of the company
Lecture 3
- Organizational structure (organizing by market, by function, matrix structure)
● Organize by market:
- By customer
- By geography
- By product
Advantages:
- High responsiveness to changes in customer preferences and market conditions
Disadvantages:
- Duplication of functions and costs
- Information flow across markets
● Organize by function
- CEO
- CFO
- Etc.
Advantages:
- Efficiency in executing the functions