Lesson 3 | Connective Tissue
● has more abundant and irregularly branched
cytoplasm, containing much rough endoplasmic
Topic Outline:
● Connective Tissue reticulum (RER) and a well developed Golgi
● Components of Connective Tissue apparatus, with a large, ovoid, euchromatic nucleus
● Types of Connective Tissue and a prominent nucleolus.
2) Fibrocyte (quiescent cell)
● inactive form of Fibroblast
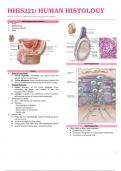
Connective Tissue
● smaller than the active fibroblast, is usually
● Connective tissue is specialized to physically support and
spindle-shaped with fewer processes, much less
connect other tissues and maintain the water required for
RER, and a darker, more heterochromatic nucleus
metabolite diffusion to and from cells.
3) Adipocytes (fat cells)
● Cells of connective tissue is scattered throughout the
● very large cells specialized for storage of triglycerides
extracellular matrix (consists of large protein fibers, and
● they predominate in a specialized form of connective
glycoproteins, attached to the basal membrane)
tissue called adipose tissue.
General Characteristics
4) Mesenchymal Cells
1) Most abundant tissue in the body
● Mesenchyme is the embryological tissue from which
2) Major constituent of connective tissue is the extracellular
all types of supporting/connective tissue are derived.
matrix (ECM)
● are relatively unspecialised and are capable of
differentiation into all supporting tissue cell types.
● have an irregular, star (stellate) or spindle (fusiform)
shape, with delicate branching cytoplasmic
extensions which form an interlacing network
throughout the tissue.
● nuclei have dispersed chromatin and visible nucleoli.
3) All connective tissue has 3 components
● The matrix consists almost exclusively of
● Cells
blue-staining ground substance without mature fibers,
● Ground Substance
facilitating diffusion of metabolites to and from
● Fibers
developing tissues.
4) Originate from embryonic mesenchyme
5) Macrophages
Functions
● Phagocytic cell of the connective tissue
1) Responsible for attachment of one tissue to another.
● short-lived cells that differentiate in connective tissue
Ex: Ligaments, Tendons
from precursor cells called monocytes
2) Transport of fluids and materials
● function in ECM turnover, phagocytosis of dead cells
Ex: Blood
and debris, and antigen presentation to lymphocytes;
3) Defending the body from invading microorganism
secretion of growth factors, cytokines, and other
immune
agents
4) Storage of materials
● “Histiocytes”
Ex: Fat
5) Establishing a structural framework for the body
Ex. Bones
Components of Connective Tissue
I. Cells of Connective Tissue
1) Fibroblasts
● the major and most abundant cells of connective
tissue proper
● are elongated, irregularly shaped cells with oval nuclei
that synthesize and secrete most components of the
ECM.
● targets of many families of proteins called growth
factors that influence cell growth and differentiation.
● involved in wound healing, sometimes called
myofibroblasts
1