FLG 221: Pulmonary Physiology
Introduction
- Air movement between environment and cells
- Functions of the respiratory system:
1. Exchange of gases between environment and blood (CO2 and O2)
2. Homeostasis (body pH)
3. Protection against pathogens
4. Vocalization
- Without food for 3 weeks
- Without water for 3 – 4 days
- Without oxygen for 3 – 6 minutes after which brain damage and death results
- Respiratory system main function: O2 ↔ CO2
Structural classification
Functional classification
,Structure and function:
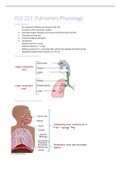
1. Nose and nasal cavity
2. Pharynx
3. Larynx
4. Trachea
5. Bronchi tree
6. Upper and lower respiratory airways
Nose and nasal cavity
- Lined with mucous membrane: contains ciliated epithelium and
mucous secreting goblet cells (mucous traps debris)
- Rich blood supply. Dilation of nasal blood vessels (cold/flu, allergy,
toxins) → oedema of mucous membranes → obstruct airways
Nasal cavity:
Functions of mucous membrane:
- Warms air (protects airway)
- Moistens/humidifies incoming air (prevents dehydration)
- Filters incoming air: nose hairs guard nostrils. Cilia and sticky mucous
entrap dust and microorganisms (cilia move debris towards pharynx)
Pharynx (throat)
- Functions as common passage for:
o transport of food from oral cavity → oesophagus
o transport of air from nasal cavity → larynx
- During swallowing soft palate is raised reflexly: prevents food from entering nasal cavity. Larynx is
elevated and breathing is inhibited reflexly: prevents food entering trachea → “choking
Larynx (voice box)
- Continuous → trachea (superior)
- The functions of the larynx:
o To act as a switching mechanism to route air (lowered) and food (elevated) into the proper
channels
o Voice production
- Inner surface of larynx: mucous membrane
, o Traps debris not filtered by nasal cavity
Trachea (windpipe)
- Larynx → Trachea → Primary Bronchi
- C-shaped cartilaginous rings: gives firmness to the wall, prevents airways from collapsing
- Mucous membrane: lined with ciliated columnar epithelium (contain goblet cells)
- Also responsible for filtering incoming air (mucous traps, cilia propels)
Bronchial tree
- Trachea → Right and Left primary bronchi
- Bronchi: lined with ciliated columnar epithelium
- Secondary bronchi → tertiary bronchi → bronchioles → terminal bronchioles (transition of conducting
to respiratory zone where gas exchange takes place)→ respiratory bronchioles (smooth muscle)→
alveolar ducts
- Smooth muscle & elastic fibres
As branching becomes more numerous the wall thins out. Alveoli design allows for increased surface area
The conducting airways
- The upper airways and bronchi condition air before → alveoli.
- Conditioning:
- Warming of air (37C): Ensures core body temp does not change & alveoli not damaged by cold air
- Adding water vapour (humidifying – prevents dehydration)
- Filtering out foreign material: ↓ viruses, bacteria & foreign inorganic particles so do not reach alveoli
(throughout airway)
Cells of the conducting airways
1. Ciliated columnar epithelial cells: mucociliary movement. Sweep foreign substances upwards
(towards pharynx)
2. Mucus secreting goblet cells: produce mucins. Mucins play added role in innate immunity of mucosa –
proteins
3. Serous cells: found in airway epithelium. Produce lysozymes, IgA – antimicrobials
4. Clara cells: found in bronchioles. Produce antiinflammatory substances (phospolipase A2 inhibitor)
5. Other cells: neuroendocrine cells (regulate smooth muscle function and growth)
, Lungs
- Lungs: exchange surface
o Surface area: 75 m2
o Thin walled
o Moist
o Enclosed by pleural membranes (pleural fluid – in between)
- Occupy most of the thoracic cavity
- Ribs & skin protect
- Right lung three lobes Left lung two lobes
The Pleura
- A double-layered sac surrounding each lung
o Parietal pleura - outer membrane which is attached to the inner surface of the thoracic wall
o Visceral pleura - membrane that covers the surface of each lung (inner membrane)
- Pleural fluid
o forms a pleural seal that holds the outer surface of the lungs against the inner surface of the
thoracic wall
o Reduces friction between pleural membranes
Introduction
- Air movement between environment and cells
- Functions of the respiratory system:
1. Exchange of gases between environment and blood (CO2 and O2)
2. Homeostasis (body pH)
3. Protection against pathogens
4. Vocalization
- Without food for 3 weeks
- Without water for 3 – 4 days
- Without oxygen for 3 – 6 minutes after which brain damage and death results
- Respiratory system main function: O2 ↔ CO2
Structural classification
Functional classification
,Structure and function:
1. Nose and nasal cavity
2. Pharynx
3. Larynx
4. Trachea
5. Bronchi tree
6. Upper and lower respiratory airways
Nose and nasal cavity
- Lined with mucous membrane: contains ciliated epithelium and
mucous secreting goblet cells (mucous traps debris)
- Rich blood supply. Dilation of nasal blood vessels (cold/flu, allergy,
toxins) → oedema of mucous membranes → obstruct airways
Nasal cavity:
Functions of mucous membrane:
- Warms air (protects airway)
- Moistens/humidifies incoming air (prevents dehydration)
- Filters incoming air: nose hairs guard nostrils. Cilia and sticky mucous
entrap dust and microorganisms (cilia move debris towards pharynx)
Pharynx (throat)
- Functions as common passage for:
o transport of food from oral cavity → oesophagus
o transport of air from nasal cavity → larynx
- During swallowing soft palate is raised reflexly: prevents food from entering nasal cavity. Larynx is
elevated and breathing is inhibited reflexly: prevents food entering trachea → “choking
Larynx (voice box)
- Continuous → trachea (superior)
- The functions of the larynx:
o To act as a switching mechanism to route air (lowered) and food (elevated) into the proper
channels
o Voice production
- Inner surface of larynx: mucous membrane
, o Traps debris not filtered by nasal cavity
Trachea (windpipe)
- Larynx → Trachea → Primary Bronchi
- C-shaped cartilaginous rings: gives firmness to the wall, prevents airways from collapsing
- Mucous membrane: lined with ciliated columnar epithelium (contain goblet cells)
- Also responsible for filtering incoming air (mucous traps, cilia propels)
Bronchial tree
- Trachea → Right and Left primary bronchi
- Bronchi: lined with ciliated columnar epithelium
- Secondary bronchi → tertiary bronchi → bronchioles → terminal bronchioles (transition of conducting
to respiratory zone where gas exchange takes place)→ respiratory bronchioles (smooth muscle)→
alveolar ducts
- Smooth muscle & elastic fibres
As branching becomes more numerous the wall thins out. Alveoli design allows for increased surface area
The conducting airways
- The upper airways and bronchi condition air before → alveoli.
- Conditioning:
- Warming of air (37C): Ensures core body temp does not change & alveoli not damaged by cold air
- Adding water vapour (humidifying – prevents dehydration)
- Filtering out foreign material: ↓ viruses, bacteria & foreign inorganic particles so do not reach alveoli
(throughout airway)
Cells of the conducting airways
1. Ciliated columnar epithelial cells: mucociliary movement. Sweep foreign substances upwards
(towards pharynx)
2. Mucus secreting goblet cells: produce mucins. Mucins play added role in innate immunity of mucosa –
proteins
3. Serous cells: found in airway epithelium. Produce lysozymes, IgA – antimicrobials
4. Clara cells: found in bronchioles. Produce antiinflammatory substances (phospolipase A2 inhibitor)
5. Other cells: neuroendocrine cells (regulate smooth muscle function and growth)
, Lungs
- Lungs: exchange surface
o Surface area: 75 m2
o Thin walled
o Moist
o Enclosed by pleural membranes (pleural fluid – in between)
- Occupy most of the thoracic cavity
- Ribs & skin protect
- Right lung three lobes Left lung two lobes
The Pleura
- A double-layered sac surrounding each lung
o Parietal pleura - outer membrane which is attached to the inner surface of the thoracic wall
o Visceral pleura - membrane that covers the surface of each lung (inner membrane)
- Pleural fluid
o forms a pleural seal that holds the outer surface of the lungs against the inner surface of the
thoracic wall
o Reduces friction between pleural membranes